Simplex polymerase chain reaction (PCR)
involves
the exponential amplification of a single locus and requires the presence of
a
single set of primers flanking the target region. An example of human OGG1
genotyping by simplex PCR-RFLP is provided below.
What is OGG1?
The human OGG1 gene is localized on chromosome 3p25, and encodes a DNA glycosylase that excises 8-hydroxyguanine (8-OH-G) from oxidatively-damaged DNA through base excision repair. 8-OH-G is a major form of oxidative DNA damage induced by reactive free radicals. It is higly mutagenic in vitro and in vivo, yielding G:C to T:A transversion, since it directs the incorporation of cytosine and adenine nucleotides opposite the lesion.
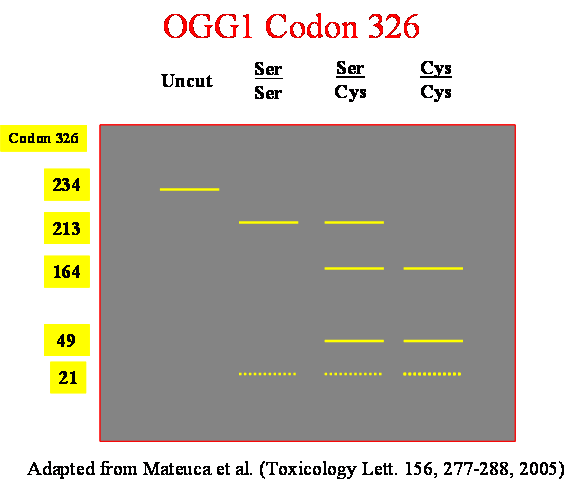
Polymorphism analysis for OGG1 codon 326:
● Genomic DNA is isolated from whole blood by means of the QIAamp Blood Mini/Midi Kit (QIAGEN).
● Primers were designed to encompass the Ser326Cys polymorphic site within the OGG1 gene.
● PCR yields a 234 bp product. 1h digestion at 37°C with the Fnu4HI restriction enzyme results in 213 and 21 bp products for the Ser alllele, and 164, 46 and 21 bp products for the Cys allele.
● After 1.5h 120 V electrophoresis through a 2% agarose gel, DNA fragments are visualised with ethidium bromide.
